What Are Zero Emissions and why it matters
Zero emissions refer to the complete elimination of greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2), from human activities. This means that no harmful pollutants are released into the atmosphere from energy production, transportation, manufacturing, or other industrial processes. Achieving zero emissions is essential to mitigating the impacts of global warming and protecting ecosystems.
The primary driver behind zero emissions is the urgent need to curb climate change. Rising global temperatures are causing more frequent and severe natural disasters, threatening biodiversity, and affecting human health. To prevent catastrophic impacts, the international community has set ambitious targets, such as the Paris Agreement’s goal of limiting global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
Sustainability in-line with business development
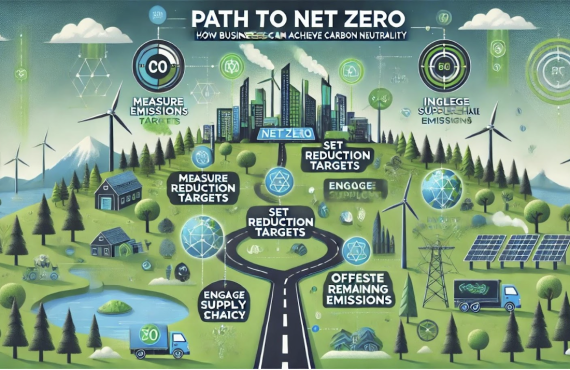
- Measuring the emissions: This process often involves considering Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions, according to the Green House Gas (GHG) protocol, which respectively cover direct emissions from owned sources, indirect emissions from purchased electricity, and indirect emissions from the wider value chain.
- Setting emission targets: Businesses can set realistic and actionable reduction targets. It is crucial to align these targets with international standards as set by the Paris agreement.
- Installing reduction strategies: This could include steps like enhancing energy efficiency, adopting green building practices, and optimising transportation.
- Monitoring and reporting: There are several global frameworks that are now being used for reporting the emission data generated by an enterprise. Framework such as Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR), Global reporting initiative (GRI), Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD).
India’s contributions towards zero emissions
India has committed a target of net-zero by 2070 as part of its nationally determined contributions (NDC) during the conference of parties (COP) 26 held in Glasgow, UK.
India’s renewable targets have steadily become more ambitious, from 175 GW by 2022 declared at Paris, to 450 GW by 2030 at the UN Climate Summit, and now 500 GW by 2030, announced at COP26
The NDC’s have eight other targets with a timeline of 2030, with a focus on increasing its carbon sink and reducing emissions up to 50% so as to be able to easily accommodate the future net-zero vision.
Conclusion
Achieving zero emissions is no small feat, but it is essential for the health of our planet and future generations. Through innovation, policy changes, and collective action, we can create a sustainable future where zero emissions are not just a goal but a reality. Let’s work together to make it happen!